Europejski System Opisu Kształcenia Językowego. Co oznaczają poziomy CEFR?
Co oznacza poziom znajomości jezyka na poziomie A, B czy C? Skrót CEFR pochodzi od Common European Framework of Reference for Languages. Jest to dokument opracowany przez Radę Europy , w którym opisano proces nabywania umiejętności czytania, pisania, słuchania i mówienia na 6 poziomach w 3 grupach dla każdego z języków krajów UE:
- A1 – A2 (poziom podstawowy)
- B1 – B2 (poziom samodzielności)
- C1 – C2 (poziom biegłości)
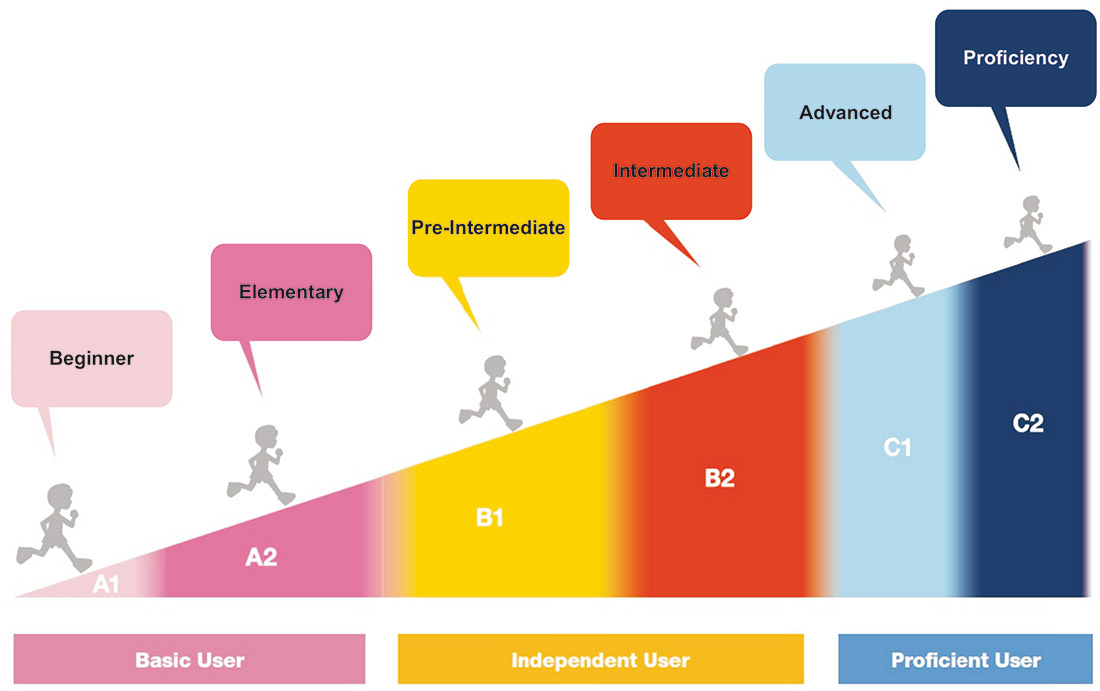 Poziom A0 oznacza osobę początkującą, która uczy się języka od podstaw. Poziom B2 + (Upper-Intermediate) to faza przejściowa pomiędzy B2 a C1 i stanowi bardzo solidne przygotowanie do egzaminów językowych np. First Certificate in English (FCE) oraz późniejszych Cambridge Advanced English (CAE – C1) bądź Cambridge Proficiency English (CPE – C2).
Poziom A0 oznacza osobę początkującą, która uczy się języka od podstaw. Poziom B2 + (Upper-Intermediate) to faza przejściowa pomiędzy B2 a C1 i stanowi bardzo solidne przygotowanie do egzaminów językowych np. First Certificate in English (FCE) oraz późniejszych Cambridge Advanced English (CAE – C1) bądź Cambridge Proficiency English (CPE – C2).
Poziom: A0-A1
*Subject Personal Pronouns
*The Verb „To Be”
*The Verb „Have Got”
*Object Pronouns
*There Is -Are /Some – Any – No
*Plurals – Countables and Uncountables
*A lot of -Much Many / (A) little – (A) few
*Articles (A/An-The / This – That – These – Those
*Possessives (Possessive case / Possessive adjectives)
*Prepositions of time
*Prepositions of place
*The Imperative
*Present Simple
*Present Continuous
*Past Simple (Was/Were – Had)
*Past Simple (Regular and Irregular Verbs)
*The Future (Will – Be Going to – Present Continuous)
*Adjectives and Adverbs / Comparisons
*Adverbs of frequency
*Object and Subject Questions
*Modal Verbs
*Infinitive / Gerund
Poziom: A1-A2
*Present Continuous – Present Simple
*Present Perfect – Past Simple
*Past Simple – Used to
*Past Continuous – Past Simple
*Past Perfect
*The Future (Future Simple – Be qoing to – Present Continuous)
*Present Perfect Continuous
*Relatives
*Pronouns,
*Modal Verbs (Be able to)
*The Infinitive – The ‘-ing form’
*Passive Voice
*Reported Speech
*Conditionals
*Adjectives – Adverbs -Comparisons
*Nouns – Articles
*Some/Any/No – A lot of/Much/Many /(A) little /(A) few
*Prepositions of movement
*Linking Words
Poziom: A2-B1
*Present Forms
*Past Forms
*Future Forms
*Infinitive – Too/Enough – The -ing form – Participles
*Modal Verbs
*The Passive
*Clauses (of time – of result – of reason – of purpose – of contrast – of manner)
*Conditionals -Wishes
*Relatives
*Reported Speech
*Have Something Done
*Nouns – Compound Nouns Articles
*The Indefinite / Definite Article
*Adjectives -Adverbs – Comparisons
*Pronouns – Possessives – Demonstratives – Quantifiers
*Wh-Questions – Object/Subject Questions – Negative Questions – Indirect Questions –
*Questions Tags
*Prepositions
*Linking Words
*Phrasal verbs
*Word Formation
Poziom: B1-B2
*Tenses
*Stative Verbs
*Infinitive/The-ing form/Too-Enough
*Participles
*Adjectives – Adverbs – Gradable adverbs – Comparisons
*Nouns – Collective Nouns – Articles –
*Word Formation
*Participles
*Modal Verbs
*Past Modals
*Perfect Modals,The Passive – Have Something Done
*Emphasis
*Inversion
*Conditionals -Wishes – Unreal Past
*Clauses – Linking Words
*Pronouns – Possessives
*Questions
*Demonstratives
*Phrasal verbs
*Often confused words
*False Friends
Poziom: B2-C1
*Open Cloze
*Key Word Transformations
*Word Formation – Prefixes and Suffixes
*Splitting phrasal verbs
*Prepositional phrases
*Derivatives
*Idioms and fixed phrases
*Words with multiple meanings
Przyjmuje się, iż przejście z jednego poziomu na drugi zajmuje średnio około 120-200 godzin. Zależy to od bardzo wielu czynników, ale jednym z najważniejszych jest intensywność nauki. Im wyższa, tym proces nabywania języka jest szybszy (zmiana czynności elektrycznej mózgu, zmiany w istocie szarej mózgu, wytworzenie połączeń neuronalnych, wytworzenie obiegu informacji, głębokie przetwarzanie informacji).
Poziom C2 (Proficiency) – biegłość na poziomie rodzimego użytkownika.
Oznacza to nabycie znajomości języka umożliwiającej radzenie sobie np. ze specjalistyczną komunikacją i pisaniem nawet na poziomie akademickim. Użytkownik posługuje się językiem i zrozumie praktycznie wszystko co usłyszy lub przeczyta.
Potrafi streszczać informacje z innych źródeł, pisanych lub mówionych w sposób spójny, odtwarzając zawarte w nich tezy i wyjaśnienia. Potrafi wyrażać swoje myśli bardzo płynnie, spontanicznie i precyzyjnie, subtelnie różnicując odcienie znaczeniowe nawet w bardziej złożonych wypowiedziach.
Funkcje językowe na każdym z poziomów:
Poziom A0-A1
*Describing habits and routines
*Giving personal information
*Greetings
*Telling the time
*Understanding and using numbers
*Understanding and using prices
Poziom A1-A2
*Checking understanding
*Describing experiences and events
*Describing feelings and emotion,
*Describing places
*Expressing opinions; language of agreeing and disagreeing
*Initiating and closing conversation
*Managing interaction (interrupting, changing topic, resuming or continuing)
Poziom A2-B1
*Critiquing and reviewing
*Describing experiences
*Describing feelings and emotions
*Describing hopes and plans
*Developing an argument
*Encouraging and inviting another speaker to continue, come in
*Expressing abstract ideas
*Expressing agreement and disagreement
*Expressing opinions
*Expressing reaction, e.g. indifference Interacting informally, reacting, expressing interest, sympathy, surprise etc.
*Opinion, justification
*Speculating
*Taking the initiative in interaction
*Synthesizing, evaluating, glossing information
Poziom B1-B2
*Conceding a point
*Critiquing and reviewing constructively
*Defending a point of view persuasively
*Developing an argument systematically
*Emphasizing a point, feeling, issue
*Expressing attitudes and feelings precisely
*Expressing certainty, probability, doubt
*Expressing opinions tentatively, hedging
*Expressing reaction, e.g. indifference
*Expressing shades of opinion and certainty
*Responding to counterarguments
*Speculating and hypothesising about causes, consequences etc.
*Synthesising, evaluating and glossing information.
Poziom B2-C1
*Accepting/rejecting suggestions
*Asking for further information
*Asking for and promising discretion
*Comparing
*Debating
*Discussing opinions
*Discussing pros & cons
*Evaluating
*Exchanging opinions
*Expressing approval and disapproval
*Expressing surprise
*Expressing opinions
*Expressing hesitation
*Expressing agreement and disagreement
*Expressing an alternative viewpoint
*Giving advice
*Giving instructions
*Insisting on a point
*Interrupting
*Introducing news
*Inviting somebody to give their opinion
*Making, rearranging & cancelling, appointments
*Making recommendations
*Making choices
*Making suggestions
*Making decisions
*Making predictions
*Making assumptions
*Sharing information
*Speculating
*Suggesting alternatives
*Telephone conversations.



















